Description:
Source(s):
Description: |
Source(s): |
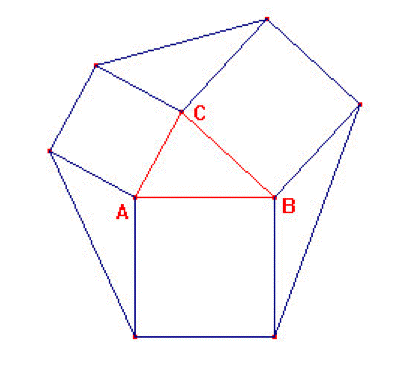
| ABC est un triangle quelconque. A l’extérieur du triangle, trois carrés ont été construits sur chacun des trois côtés. On construit trois nouveaux triangles en reliant les sommets libres des carrés. Comparer l’aire de chacun des trois triangles avec l’aire du triangle ABC. | (Pedemonte 2002, thèse) |
ABC is a triangle. Three
exteriors squares are constructed on
the triangle’s sides. The free points of the squares are
connected defining three other triangles. Compare the areas of these
triangles with the area of triangle ABC (see figure). |
(Pedemonte 2003, CERME) |
|
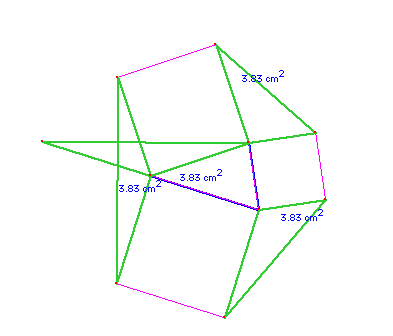
In a dynamic geometry environment it is simple to discover that the areas of all four triangles are the same. The problem is then to prove or explain this. One approach is to rotate an outer triangle 90 degrees around the vertex it shares with the inner triangle. It is then easy to see that the two triangles have the same height and same base, and hence the same area. |
 |
Supported by a research grant from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada
Page last updated July 2008 by David Reid